Editor’s Note: Spring is upon us! HMNS Astronomer James Wooten reminds us to adjust our clocks and explains why we observe Daylight Savings Time.
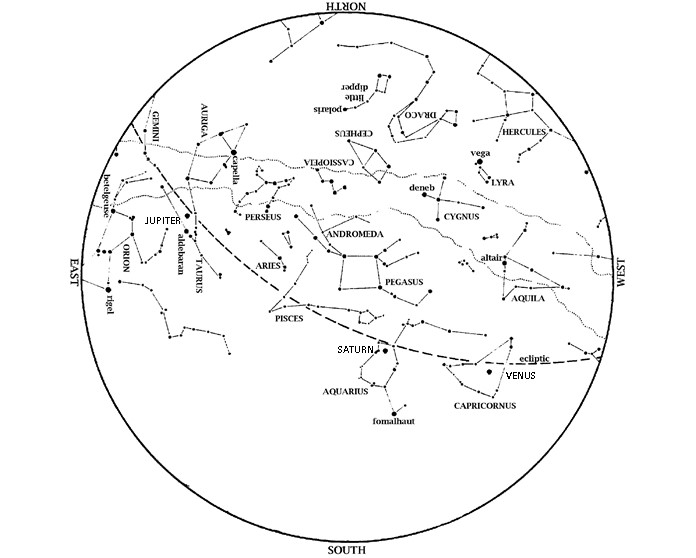
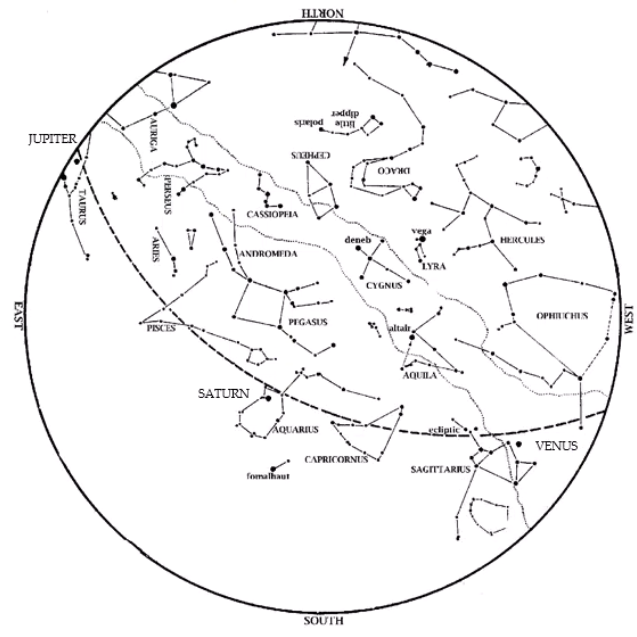
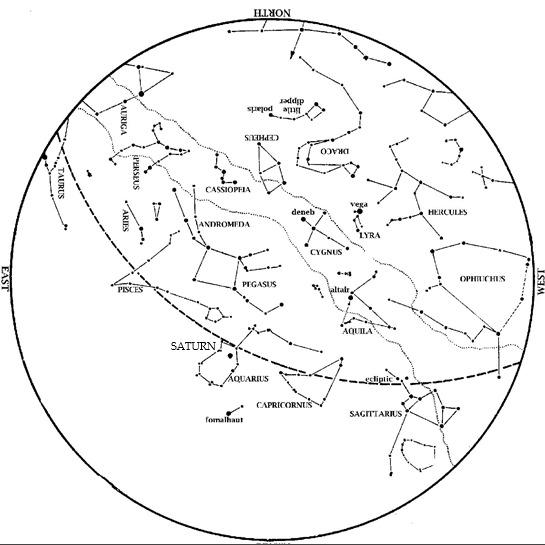
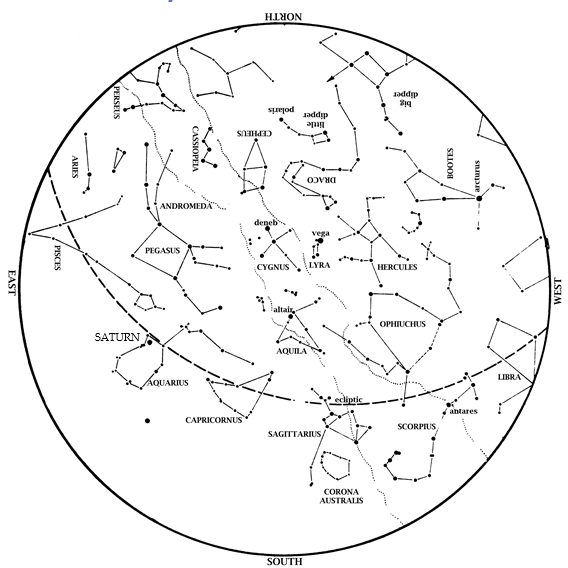
Jupiter is prominent high in the sky, high in the west at nightfall. No star at night is as bright.
Mercury also enters the evening sky this month. Start looking west at dusk during our Spring Break week (starting March 11), and keep looking the week after that. Look west at dusk, along a line from Jupiter towards where sunset occurred.
Venus remains in the morning sky. Look for it low in the southeast at dawn this month. Venus appears slightly lower to the horizon each morning. By month’s end, it is becoming lost in the Sun’s glare.
Mars continues to emerge slowly from the Sun’s glare this month. It is still low to the horizon at dawn, though a bit higher than last month.
Saturn is lost in the Sun’s glare and out of sight most of the month. Perhaps you can see it low to the horizon at dawn the last week of March.

Brilliant winter stars shift towards the southwest during March. Dazzling Orion is almost due south at dusk. His three-starred belt is halfway between reddish Betelgeuse and bluish Rigel. Orion’s belt points up to Aldebaran in Taurus the Bull. To Orion’s upper left are the twin stars Castor and Pollux, marking the heads of Gemini, the Twins. You can find Sirius, the brightest star we ever see at night, by drawing a line from Orion’s belt towards the horizon. To Orion’s left, about level with Betelgeuse, is Procyon, the Little Dog Star.
Under Sirius and low to the southern horizon this month is a star that most Americans never get to see—Canopus. Representing the bottom (keel) of the legendary ship Argo, Canopus is the second brightest star ever visible at night. Thus, it is clearly noticeable along the southern horizon on February and March evenings. However, you must be south of 37 degrees north to see Canopus rise. (This is the line that divides Utah, Colorado, and Kansas from Arizona, New Mexico, and Oklahoma.)
Joining the winter stars are stars of spring rising in the east. Look for Leo, the Lion at dusk. Later in the evening, extend the Big Dipper’s handle to ‘Arc to Arcturus’ and then ‘speed on to Spica’; these stars rise at about 10:00 in early March but by 9pm on the 31st.
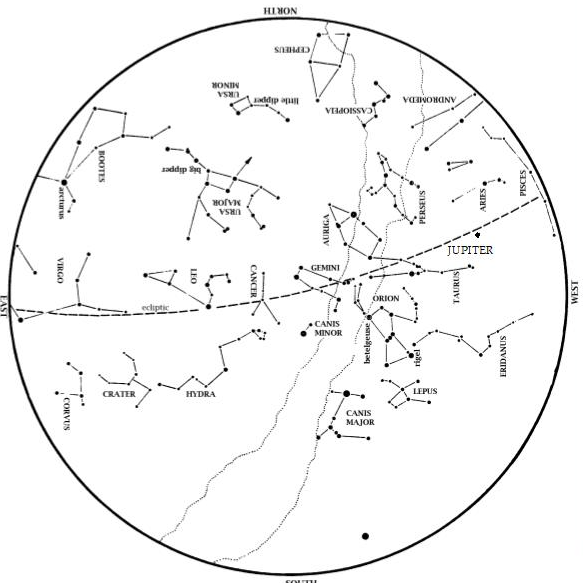
Taurus, the Bull, is now high in the west. Dazzling Orion, the Hunter is high in the southwest, with his two dogs behind him. Sirius, the Big Dog Star, is the brightest star we ever see at night. Look for Canopus on the southern horizon below Sirius. In the north, the Big Dipper is higher in the sky. Leo, the Lion, and Virgo, the Virgin, rise in the east. These stars, along with Arcturus, announce the coming spring.
Moon Phases in March 2024
Last Quarter Mar. 3, 9:24 a.m.
New Mar. 10, 4:00 a.m.
1st Quarter Mar. 16, 11:11 p.m.
Full Mar. 25, 2:00 a.m.
Sunday, March 10, is the second Sunday of March. Accordingly, Daylight Saving Time begins at 2:00 am on this date. (The time jumps from 1:59 am to 3:00, skipping the 2:00 hour). Don’t forget to set your clocks forward one hour Saturday night, March 9!
At 10:07 pm on Tuesday, March 19, the Sun appears directly overhead at the equator, shifting northwards. Thus, this is our spring equinox, a day when everyone in the world gets the same amount of daylight. This is also when daytime, which has been lengthening since the winter solstice, becomes longer than night. Below the equator, of course, the reverse is true. There, daytime has been shortening since late December and becomes shorter than night at the equinox. Autumn, rather than spring, is underway.
Our George Observatory is now open every Saturday night for observing! Purchase tickets in advance on our website.
Clear Skies!
Looking for February’s sky happenings? Click here.